Solar Panel Recycling – New Market Focus for the Future?

Introduction: Lifetime of a solar panel
Typically, the solar panels widely used today have a lifespan of 25 to 30 years. A large number of solar photovoltaic (PV) projects were built in the past 20 years and will soon reach the end of their lifespan. Over the course of the PV panels’ 30-year life, their efficiency and power capacity will decrease, with around 8% of efficiency being lost after 25 years. Although some PV panels have been known to last longer than their estimated lifespan, the issue of waste management and recycling still needs to be addressed in the PV industry. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), global PV waste will increase from less than 250,000 tonnes in 2016 to 6 million tonnes in 2050, which is roughly equivalent to the new installed capacity of the year (6.7 million).
As more and more solar PV projects are being installed worldwide, many countries are seeking to transition to a more renewable energy mix, with solar photovoltaics being the cheapest option. The problem of how to recycle the components of PV systems remains a significant concern for developers, installers, and end users alike.
Legal requirements, the industry, and the PV Cycle Organisation
Globally, governments have instituted various directives regarding the management of e-waste. In 2003, the European Union enacted the Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment Directive (WEEE Directive) and the Restriction of Hazardous Substances Directive (ROHS Directive), which obligate producers and distributors to comply with regulations for e-waste disposal. As a consequence of the WEEE Directive, solar panels are considered hazardous waste that necessitates proper disposal. China, following suit, instituted the Management of Collection and Disposal of Waste Electrical and Electronic Products (Chinese WEEE regulations) in 2011. The United States, on the other hand, lacks a comprehensive policy for WEEE management and instead relies on companies voluntarily following environmental guidelines.
The proliferation of PV disposal and recycling has spurred numerous companies to enter the PV recycling industry. PV Cycle, a non-profit organisation with a membership-based structure, provides waste management and legal compliance services specific to PV, and many of the world’s leading PV panel suppliers are members of this organisation. As an example, Veolia, in collaboration with PV Cycle, inaugurated its first PV panel recycling service in France in 2017 with the objective of reutilising the glass, aluminum frame, plastic, and silicon in various industrial sectors.
Components of a solar panel
Prior to delving into the subject of solar panel recycling, let’s first examine the components of a solar panel. Typically, there are two primary categories of solar panels: the c-silicon panel, which encompasses mono- and poly-types and constitutes the most prevalent type utilised in solar photovoltaic (PV) projects, and the thin-film panel. I will elaborate on the distinctions between these panel types in a subsequent blog post. The illustration below compares the composition of c-silicon and thin-film panels.
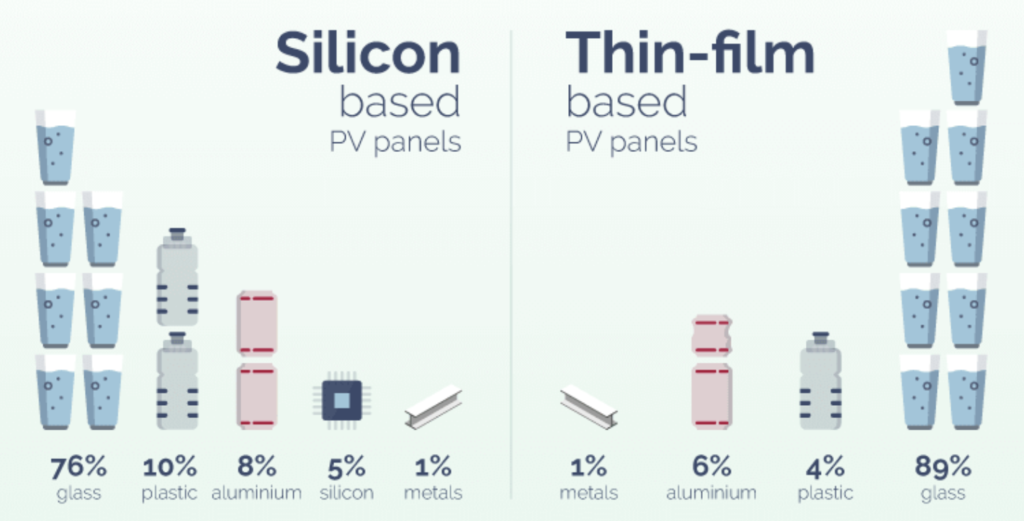
The disparities between c-silicon-based panels and thin-film panels result in a differentiation of their respective recycling processes.
Recycling process
The recycling process generally has four stages:
- Collection and transport of PV panels to recycling facilities;
- Initial categorisation and handling;
- Waste management specific to the panel types;
- Finalisation and material recovery for reuse.
The recycling procedure for c-silicon panels typically begins with the disassembling of the aluminum frame and connecting components. The external metals, constituting approximately 95% of the panel, are typically repurposed for remoulding, as well as the glass. Subsequently, the photovoltaic cells are separated, usually via a thermal process, and a substantial proportion, around 85%, of the silicon can be recovered for the production of new silicon modules.
As for thin-film panels, given their properties, they are initially shredded, and a rotating screw is used to separate the solid and liquid portions. The liquid component is processed to ensure the recovery of roughly 95% of the precious semiconductor materials, while the solid component undergoes further treatment to leave only glass for reuse.
Outlook of Recycling Solar Panels
In my opinion, the prospects of solar panel recycling have many aspects. Firstly, it creates a lucrative market opportunity for the renewable energy industry; currently, there are only a few companies engaged in PV panel waste management, however, with the projected 6 million tonnes of waste by 2050, demand for this service will surge in the coming years. Secondly, advancements in technology may lead to the development of more efficient recycling methods for both c-silicon and thin-film solar panels, as well as the advent of new types of panels that are easier to recycle. Thirdly, similar to recycled plastics, the availability of recycled solar panels in the market may prompt generation companies to adopt them as a means of projecting an eco-friendly image, thereby appealing to consumers who are more environmentally conscious.
While solar panel recycling is still in its infancy within the industry, the future holds immense potential.
References
https://www.greenmatch.co.uk/blog/2017/10/the-opportunities-of-solar-panel-recycling
https://www.technologyreview.com/2021/08/19/1032215/solar-panels-recycling/
https://www.greentechrenewables.com/article/can-solar-panels-be-recycled
https://www.theecoexperts.co.uk/solar-panels/solar-panel-recycling
https://www.engie.com/en/activities/renewable-energies/solar-energy/recycling-solar-panels
https://pvcycle.org/about-pv-cycle/#
https://www.idealhome.co.uk/project-planning/are-solar-panels-recyclable-302524
https://www.veolia.com/en/solution/recycling-photovoltaic-panels-technology-unique-france

0 Comments